Understanding Lab-Grown Meat: A Sustainable Alternative
Lab-grown meat, commonly known as cultured or cell-based meat, represents a revolutionary change in our approach to food production. By cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, this cutting-edge technique provides a sustainable alternative to traditional meat farming. Imagine relishing the taste and texture of your favourite meats without the significant environmental impact or ethical dilemmas associated with conventional livestock farming. As consumers grow increasingly aware of their dietary choices, the demand for lab-grown options has escalated, signalling a potential transformation in global eating habits towards more sustainable practices.
One of the most compelling advantages of lab-grown meat is its markedly lower environmental impact. Conventional meat production is infamous for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and excessive water usage. In contrast, lab-grown meat has the capacity to substantially reduce these negative effects, fostering a more sustainable food system. Additionally, this innovative production method eliminates the need for animal slaughter, catering to a growing demographic of ethical consumers who place high importance on animal welfare. By integrating advanced technology with culinary traditions, lab-grown meat meets both ethical and environmental demands, paving the way for a sustainable future in food production.
The future of food is not merely a passing trend; it represents a significant paradigm shift. Lab-grown meat has the potential to redefine our relationship with food, prompting individuals worldwide to reconsider their dietary choices. With the incorporation of sophisticated technology alongside a rising awareness of sustainability, the possibilities are boundless. Envision a world where meat can be produced with minimal environmental degradation, ensuring that future generations can relish it as a staple in their diets.
Nonetheless, the path to widespread acceptance and adoption of lab-grown meat is fraught with challenges. The high production costs remain a major obstacle, making it imperative for innovators to discover efficient methods to scale up production. Furthermore, the regulatory approval processes can impede market entry, as governments globally grapple with how to classify and regulate this new category of food. Overcoming these challenges will be vital to make lab-grown meat a widely accessible and mainstream option for consumers seeking sustainable alternatives.
Key Ingredients for Lab-Grown Meat Production
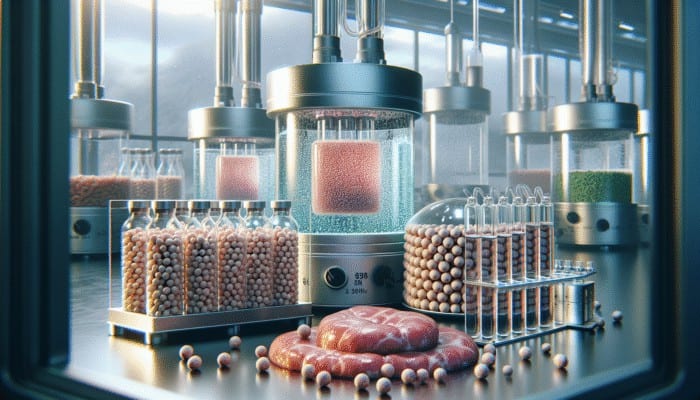

The production of lab-grown meat relies heavily on a distinct combination of ingredients that facilitate cell growth and development. At the core of this process are the protein sources utilized in the culture medium. These elements are crucial for nourishing the animal cells as they proliferate and mature into muscle tissue. Commonly used plant-based proteins, such as soy and pea protein, are often incorporated to provide essential amino acids, while some techniques may include animal serum to foster robust growth. The selection of protein sources not only impacts the texture and flavour of the final product but also its overall nutritional profile.
Growth factors are another critical element in the cultivation of lab-grown meat. These biomolecules are essential for stimulating cell division and differentiation, ensuring that the cells grow healthily and effectively. Without appropriate growth factors, muscle tissue development can be hindered, leading to a product that falls short of consumer quality expectations. Researchers are constantly investigating innovative methods to optimise these growth factors, aiming to boost both the efficiency and yield of lab-grown meat production. This focus on enhancing growth factors is vital, as it can greatly affect the texture and flavour, aligning them more closely with traditional meat experiences.
Moreover, scaffolding materials play a significant role in creating the desired structure of lab-grown meat. These materials provide a three-dimensional framework that supports cell growth and mimics the natural architecture of muscle tissue. By employing biodegradable scaffolds made from substances like collagen or alginate, producers can improve the texture and chewability of lab-grown meat. The choice of scaffolding material not only influences the sensory experience for consumers but also affects the overall environmental footprint of the production process.
The interplay of these essential ingredients forms the foundation of lab-grown meat production, underscoring the intricate balance between innovation and sustainability. As research in this dynamic field progresses, the pursuit of the ideal combination of proteins, growth factors, and scaffolding materials continues, paving the way for the next generation of meat alternatives that resonate with consumers across the globe.
Maximising Culinary Potential: Cooking Techniques for Lab-Grown Meat
Exploring various cooking techniques is crucial for optimising the potential of lab-grown meat, ensuring that it meets the culinary expectations of a diverse range of consumers. Grilling and roasting represent two of the most traditional methods that can be employed to enhance the flavour and texture of lab-grown meat. These techniques promote the caramelisation of natural sugars, resulting in a desirable crust and smoky flavour that closely mimics the experience of cooking conventional meats. When seasoned appropriately, grilled lab-grown meat can deliver a taste that resonates with meat enthusiasts, making it an enticing alternative for those looking to transition to more sustainable eating habits.
Searing and pan-frying are equally effective cooking methods that can lock in juiciness while developing a rich, golden exterior. The high heat generated by these techniques can create a satisfying crust, providing a hearty experience that is both visually appealing and delicious. Whether preparing burgers or stir-fried dishes, these methods can elevate the overall dining experience, showcasing lab-grown meat in innovative ways that highlight its versatility and adaptability in various culinary applications.
For those who seek precision in their cooking methods, the sous vide technique is a game-changer. This method involves sealing lab-grown meat in a vacuum bag and cooking it in a water bath at a controlled temperature, ensuring even cooking while preserving moisture. The result is tender, flavourful meat that maintains its integrity without the risk of overcooking. Sous vide allows chefs and home cooks alike to experiment with flavours and marinades, enhancing the overall taste experience. As more people become familiar with sous vide cooking, its application in preparing lab-grown meat could further popularise this sustainable food choice.
Ultimately, the cooking technique chosen will significantly influence the final dish. Each method presents unique opportunities to enhance flavours, introduce new textures, and cater to different culinary traditions from around the globe. With proper preparation, lab-grown meat can seamlessly integrate into kitchens worldwide, inviting a new generation of diners to embrace innovative food technologies that promote sustainability and culinary creativity.
Exploring Diverse Flavor Profiles of Lab-Grown Meat
Understanding and enhancing the flavour profiles of lab-grown meat is essential for its acceptance across various culinary cultures. One of the most effective methods to achieve this is through marinating techniques. A well-crafted marinade can infuse lab-grown meat with a vibrant burst of flavours, transforming it into a delectable dish that appeals to an array of taste preferences. By utilising a mix of herbs, spices, and acids, such as vinegar or citrus juice, cooks can tenderise the meat while adding depth and complexity. For example, a marinade consisting of soy sauce, garlic, and ginger not only introduces umami notes but also pairs beautifully with Asian-inspired dishes.
Spice rubs and seasonings also play a pivotal role in elevating the overall flavour of lab-grown meat. Various cultural cuisines offer rich inspiration for diverse spice combinations. Consider a classic barbecue rub that incorporates smoked paprika, cumin, and brown sugar, evoking the traditional flavours of grilled meats. Alternatively, a Mediterranean blend featuring za'atar or harissa can elevate the taste of lab-grown meat to new heights, showcasing the ingredient's versatility. These flavourings enable cooks to cater to a broad spectrum of culinary preferences, ensuring that lab-grown meat can be seamlessly integrated into a variety of cuisines.
Furthermore, sauces and condiments serve as vital companions to lab-grown meat, presenting additional opportunities to enhance flavour profiles. A rich barbecue sauce can provide a sweet and smoky glaze, while a zesty chimichurri can introduce freshness and brightness to grilled cuts. By utilising innovative sauces, chefs can transform lab-grown meat into an unforgettable dining experience that resonates with a global audience. The key is to experiment with flavours that complement the meat's natural characteristics without overwhelming them, ensuring a harmonious balance that excites the palate.
Through thoughtful cooking methods and creative flavour combinations, lab-grown meat can deliver a unique culinary experience that transcends traditional meat options. As chefs and home cooks alike delve into the possibilities, the outcome will be a diverse array of dishes that highlight the potential of lab-grown meat in contemporary cuisine, promoting both sustainability and innovation in our food choices.
Understanding the Nutritional Benefits of Lab-Grown Meat

When it comes to lab-grown meat, grasping its nutritional profile is crucial for both consumers and producers alike. One of its standout features is its high-quality protein content, which is comparable to that of traditional meat. This protein is vital for muscle growth, repair, and overall health. As more individuals seek to incorporate sustainable protein sources into their diets, lab-grown meat emerges as an appealing option that aligns with health-conscious choices. With its ability to deliver essential amino acids while being produced with a significantly lower environmental footprint, lab-grown meat is gaining recognition as a pivotal player in the future of protein consumption.
In addition to its high protein content, lab-grown meat presents opportunities for fortification with essential vitamins and minerals. Nutritional enhancements can ensure that lab-grown meat meets specific dietary needs, catering to diverse populations. For example, iron and vitamin B12 are crucial nutrients often found in traditional meat. By incorporating these vitamins into lab-grown meat, producers can create a product that not only appeals to meat lovers but also addresses potential deficiencies in vegetarian or vegan diets. This adaptability positions lab-grown meat as a valuable addition to health-focused diets on a global scale.
Dietary adaptations represent another significant aspect of lab-grown meat's appeal. With the rise of specialised diets, from low-fat to high-iron options, lab-grown meat can be tailored to meet various consumer preferences. For instance, by adjusting the fat content during production, lab-grown meat can cater to individuals seeking healthier alternatives without compromising taste. This level of customization not only broadens the consumer base but also encourages a shift towards more sustainable eating habits, aligning with the growing demand for healthier food choices.
As lab-grown meat continues to evolve, its nutritional considerations will play a vital role in its acceptance and integration into daily diets. By prioritising health benefits alongside sustainability, producers can ensure that lab-grown meat becomes a staple in households across the globe, addressing both dietary and ethical concerns while contributing to a more sustainable food future.
Innovative Recipe Ideas Featuring Lab-Grown Meat
One of the most exciting aspects of lab-grown meat lies in its culinary versatility, which allows for innovative recipe ideas that cater to a diverse array of tastes and preferences. Let’s explore a few standout recipes that showcase how lab-grown meat can be transformed into delectable meals that satisfy a range of palates.
Lab-grown meat burgers are sure to please a crowd, offering a juicy, satisfying option for those yearning for a classic meal. Begin with a base of finely ground lab-grown meat mixed with breadcrumbs, onions, and your choice of seasonings. Shape the mixture into patties and grill them to perfection. Serve on a toasted bun adorned with an assortment of toppings such as fresh lettuce, tomatoes, pickles, and gourmet sauces. The beauty of this recipe lies in its customisability; feel free to swap out traditional toppings for unique options like avocado, spicy aioli, or even grilled pineapple for an exotic twist. Lab-grown meat burgers are ideal for barbecues, weeknight dinners, or casual gatherings with friends and family.
For a more adventurous culinary experience, consider preparing lab-grown meat stir-fry. This quick and easy recipe is perfect for busy cooks seeking a healthy meal option. Sauté lab-grown meat with an array of colourful vegetables such as bell peppers, broccoli, and snap peas in a hot wok. Add a generous splash of soy sauce, along with garlic and ginger, for an explosion of flavour. Serve over steamed rice or noodles, and you have a vibrant, nutritious dish that satisfies both hunger and taste. With endless variations, lab-grown meat stir-fry can effortlessly become a household staple, providing a quick and nutritious meal option.
Lab-grown meat skewers present another exciting option, perfect for grilling enthusiasts. Marinate lab-grown meat in a mixture of olive oil, lemon juice, and herbs like rosemary or thyme for a delicious flavour infusion. Thread the marinated meat onto skewers alongside colourful vegetables such as cherry tomatoes, bell peppers, and zucchini. Grill until charred and serve with a refreshing yogurt sauce or a spicy salsa for an unforgettable feast. These skewers make for an excellent choice for outdoor gatherings, showcasing the delightful potential of lab-grown meat in a fun, shareable format.
Lastly, lab-grown meat tacos offer a fantastic opportunity for a fun and easy dinner party. Use seasoned lab-grown meat as the star ingredient, complemented by fresh salsa, guacamole, and crunchy slaw. Serve with soft or hard taco shells, allowing guests to build their own creations. This interactive dining experience invites creativity and caters to various preferences, making it an ideal choice for social gatherings. With the right ingredients, lab-grown meat tacos can transport diners to the vibrant streets of Mexico, proving that sustainable options can be both delicious and enjoyable.
As the culinary landscape embraces lab-grown meat, the possibilities for unique and exciting recipes are virtually limitless. By incorporating this innovative ingredient into everyday dishes, we can explore diverse flavour profiles while promoting a sustainable future for food that satisfies the appetites of the modern consumer.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lab-Grown Meat
What exactly is lab-grown meat?
Lab-grown meat, often referred to as cultured meat, is produced by culturing animal cells in a laboratory setting, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional meat without necessitating animal slaughter.
Is lab-grown meat healthier than conventional meat?
Lab-grown meat can be fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, potentially providing a healthier nutritional profile than conventional meat, depending on the production process and ingredients utilised.
How is lab-grown meat produced?
Lab-grown meat is created by extracting cells from actual animals, which are then cultured in a nutrient-rich medium designed to promote cell growth and development into muscle tissue.
What are the environmental advantages of lab-grown meat?
Lab-grown meat contributes to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, requires significantly less land and water, and helps decrease deforestation compared to traditional livestock farming practices.
Can lab-grown meat be cooked like regular meat?
Yes, lab-grown meat can be prepared using various cooking methods such as grilling, roasting, and pan-frying, providing a taste and texture that closely resembles conventional meat.
What are the primary challenges facing lab-grown meat?
High production costs and regulatory approval processes present significant obstacles to the widespread adoption of lab-grown meat in the global marketplace.
Is lab-grown meat safe for consumption?
Yes, lab-grown meat undergoes rigorous testing and must comply with safety regulations established by food safety authorities before it can be made available to consumers.
How does the taste of lab-grown meat compare to traditional meat?
Lab-grown meat can closely replicate the taste and texture of traditional meat, depending on the production methods and flavouring techniques employed during its preparation.
Where can I purchase lab-grown meat?
The availability of lab-grown meat varies by location, with products beginning to appear in select restaurants and stores worldwide as regulatory challenges are addressed.
Will lab-grown meat entirely replace conventional meat?
While lab-grown meat is unlikely to completely replace traditional meat, it provides a sustainable alternative that can complement existing meat production systems and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.


It’s truly fascinating to think about how lab-grown meat could reshape our food landscape. I’ve been on a journey to eat more sustainably, and the idea of enjoying familiar meat flavors without the environmental toll is incredibly appealing.
It’s great to hear you’re on a journey toward more sustainable eating. Lab-grown meat really does offer a unique opportunity to balance our desire for familiar flavors with a more environmentally friendly approach. It’s interesting how this technology could alleviate some of the largest environmental concerns associated with traditional meat production, like greenhouse gas emissions and land use.
“I’m glad to hear you’re exploring sustainable eating! If you’re curious to learn more about lab-grown meat and its benefits, check out this informative guide.”
https://cookinggods.com/DigestiveHealth
You’re tapping into something really interesting with the whole concept of lab-grown meat and sustainability. As more people, like yourself, shift toward sustainable eating, it’s clear that there’s a growing appetite for options that fit our values without sacrificing the flavors and experiences we love.
“I’m glad to hear you’re embracing sustainable eating! If you’re curious about lab-grown meat and its benefits, check out this resource to learn more about how it can fit into your journey.”
https://cookinggods.com/SmoothieRecipes
It’s fascinating to consider how lab-grown meat could reshape not just our diets, but also the entire food industry. I’ve personally been trying to reduce my meat intake due to environmental concerns, but I miss the flavors and textures of traditional meat. Lab-grown options seem like a perfect middle ground, allowing us to enjoy our favorite dishes without compromising our values.
You’ve touched on a really exciting aspect of lab-grown meat: the potential to bridge the gap between our cravings for traditional flavors and the necessity of making more sustainable choices. It’s a delicate dance, isn’t it? Balancing our taste preferences with the growing awareness of how our food choices impact the planet is a challenge many of us face.
“I’m glad to hear you’re exploring new options! If you’re curious about how lab-grown meat can fit into your lifestyle, check out this link for some delicious alternatives that stay true to the flavors you love.”
https://cookinggods.com/ChocolateHealth
While the potential of lab-grown meat as a sustainable alternative is intriguing, I find myself questioning whether it truly addresses the foundational issues behind our current food systems. The convenience of producing meat without the environmental costs is appealing, yet it raises questions about our dependency on technology in food production. Is cultivating meat at scale really the answer, or does it merely shift the existing industrial paradigm into the lab?
You raise some really important points about lab-grown meat that I think a lot of people are grappling with right now. It’s a fascinating topic, and you’re right to question whether it genuinely addresses the deeper issues in our food systems.
I find the rise of lab-grown meat quite fascinating, especially as someone who has been increasingly conscious of my dietary choices. It’s exciting to think about how this technology could help bridge the gap between our need for protein and the urgent need to address climate change. Personally, I believe this shift could redefine our relationship with food.
It’s great to hear that you’re finding the rise of lab-grown meat fascinating, especially as you become more aware of your dietary choices. The potential for this technology to offer a more sustainable source of protein is definitely promising. It might change how we view food, not just in terms of sourcing but also in how we think about the animals involved and the environment.
I’m glad you share that enthusiasm! If you’re curious to explore more about the future of lab-grown meat and its impact on our diets and the planet, check out this insightful resource.
https://cookinggods.com/SmoothieRecipes
I appreciate your perspective on the potential of lab-grown meat. It’s interesting to consider how this technology might not just alter our diets but also shift our cultural norms around food and animal welfare. Personally, I’ve been trying to become more mindful about what I eat, and the idea of lab-grown options really resonates with my growing interest in sustainable living.